Algorithms & Optimizations
Algorithms
1// Parameters
2int nerr = 0;
3int debugJ = 0;
4int debugdJ = 0;
5real umax = 0;
6
7// Algorithms tests
8{
9 func bool stop (int iter, real[int] u, real[int] g){
10 cout << " stop = " << iter << " " << u.linfty << " " << g.linfty << endl;
11 return g.linfty < 1e-5 || iter > 15;
12 }
13 // minimization of J(u) = 1./2 * sum (i+1) u_i^2 - b_i
14 real[int] b(10), u(10);
15
16 //J
17 func real J (real[int] & u){
18 real s = 0;
19 for (int i = 0; i < u.n; i++)
20 s += (i+1)*u[i]*u[i]*0.5 - b[i]*u[i];
21 if (debugJ)
22 cout << "J = " << s << ", u = " << u[0] << " " << u[1] << endl;
23 return s;
24 }
25
26 //the gradiant of J (this is a affine version (the RHS is in)
27 func real[int] DJ (real[int] &u){
28 for (int i = 0; i < u.n; i++)
29 u[i] = (i+1)*u[i];
30 if (debugdJ)
31 cout << "dJ: u = " << u[0] << " " << u[1] << " " << u[2] << endl;
32 u -= b;
33 if (debugdJ)
34 cout << "dJ-b: u = " << u[0] << " " << u[1] << " " << u[2] << endl;
35 return u; //return of global variable ok
36 }
37
38 //the gradiant of the bilinear part of J (the RHS is remove)
39 func real[int] DJ0 (real[int] &u){
40 for (int i = 0 ; i < u.n; i++)
41 u[i] = (i+1)*u[i];
42 if(debugdJ)
43 cout << "dJ0: u =" << u[0] << " " << u[1] << " " << u[2] << endl;
44 return u; //return of global variable ok
45 }
46
47 //erro calculation
48 func real error (real[int] & u, real[int] & b){
49 real s = 0;
50 for (int i = 0; i < u.n; i++)
51 s += abs((i+1)*u[i] - b[i]);
52 return s;
53 }
54
55 func real[int] matId (real[int] &u){ return u; }
56
57 int verb=5; //verbosity
58 b = 1.; //set right hand side
59 u = 0.; //set initial gest
60
61 LinearCG(DJ, u, eps=1.e-6, nbiter=20, precon=matId, verbosity=verb);
62 cout << "LinearGC (Affine) : J(u) = " << J(u) << ", err = " << error(u, b) << endl;
63 nerr += !(error(u,b) < 1e-5);
64 if(nerr) cout << "sol: u = " << u[0] << " " << u[1] << " " << u[2] << endl;
65
66 b = 1;
67 u = 0;
68 LinearCG(DJ, u, eps=1.e-15, nbiter=20, precon=matId, verbosity=verb, stop=stop);
69 cout << "LinearGC (Affine with stop) : J(u) = " << J(u) << ", err = " << error(u, b) << endl;
70 nerr += !(error(u,b) < 1e-5);
71 if(nerr) cout << "sol: u = " << u[0] << " " << u[1] << " " << u[2] << endl;
72
73 b = 1;
74 u = 0;
75 LinearCG(DJ0, u, b, eps=1.e-6, nbiter=20, precon=matId, verbosity=verb);
76 cout << "LinearGC (Linear) : J(u) = " << J(u) << ", err = " << error(u, b) << endl;
77 nerr += !(error(u,b) < 1e-5);
78 if(nerr) cout << "sol: u = " << u[0] << " " << u[1] << " " << u[2] << endl;
79
80
81 b = 1;
82 u = 0;
83 AffineGMRES(DJ, u, eps=1.e-6, nbiter=20, precon=matId, verbosity=verb);
84 cout << "AffineGMRES (Affine) : J(u) = " << J(u) << ", err = " << error(u, b) << endl;
85 nerr += !(error(u,b) < 1e-5);
86 if(nerr) cout << "sol: u = " << u[0] << " " << u[1] << " " << u[2] << endl;
87
88 b=1;
89 u=0;
90 LinearGMRES(DJ0, u, b, eps=1.e-6, nbiter=20, precon=matId, verbosity=verb);
91 cout << "LinearGMRES (Linear) : J(u) = " << J(u) << ", err = " << error(u, b) << endl;
92 nerr += !(error(u,b) < 1e-5);
93 if(nerr) cout << "sol: u = " << u[0] << " " << u[1] << " " << u[2] << endl;
94
95
96 b=1;
97 u=0;
98 NLCG(DJ, u, eps=1.e-6, nbiter=20, precon=matId, verbosity=verb);
99 cout << "NLCG: J(u) = " << J(u) << ", err = " << error(u, b) << endl;
100 nerr += !(error(u,b) < 1e-5);
101 if(nerr) cout << "sol: u =" << u[0] << " " << u[1] << " " << u[2] << endl;
102
103
104 //warning: BFGS use a full matrix of size nxn (where n=u.n)
105 b=1;
106 u=2;
107 BFGS(J, DJ, u, eps=1.e-6, nbiter=20, nbiterline=20);
108 cout << "BFGS: J(u) = " << J(u) << ", err = " << error(u, b) << endl;
109 assert(error(u,b) < 1e-5);
110 if(nerr) cout << "sol: u =" << u[0] << " " << u[1] << " " << u[2] << endl;
111
112 assert(nerr==0);
113}
114
115{ // A real non linear test
116 // Parameters
117 real a = 0.001;
118 real eps = 1e-6;
119 //f(u) = a*u + u-ln(1+u), f'(u) = a+ u/(1+u), f''(u) = 1/(1+u)^2
120 func real f(real u) { return u*a+u-log(1+u); }
121 func real df(real u) { return a+u/(1+u); }
122 func real ddf(real u) { return 1/((1+u)*(1+u)); }
123
124 // Mesh
125 mesh Th = square(20, 20);
126
127 // Fespace
128 fespace Vh(Th, P1);
129 Vh b = 1;
130 Vh u = 0;
131
132 fespace Ph(Th, P0);
133 Ph alpha; //store df(|nabla u|^2)
134
135 // The functionnal J
136 //J(u) = 1/2 int_Omega f(|nabla u|^2) - int_Omega u b
137 func real J (real[int] & u){
138 Vh w;
139 w[] = u;
140 real r = int2d(Th)(0.5*f(dx(w)*dx(w) + dy(w)*dy(w)) - b*w);
141 cout << "J(u) = " << r << " " << u.min << " " << u.max << endl;
142 return r;
143 }
144
145 // The gradiant of J
146 func real[int] dJ (real[int] & u){
147 Vh w;
148 w[] = u;
149 alpha = df(dx(w)*dx(w) + dy(w)*dy(w));
150 varf au (uh, vh)
151 = int2d(Th)(
152 alpha*(dx(w)*dx(vh) + dy(w)*dy(vh))
153 - b*vh
154 )
155 + on(1, 2, 3, 4, uh=0)
156 ;
157
158 u = au(0, Vh);
159 return u; //warning: no return of local array
160 }
161
162 // Problem
163 alpha = df(dx(u)*dx(u) + dy(u)*dy(u));
164 varf alap (uh, vh)
165 = int2d(Th)(
166 alpha*(dx(uh)*dx(vh) + dy(uh)*dy(vh))
167 )
168 + on(1, 2, 3, 4, uh=0)
169 ;
170
171 varf amass(uh, vh)
172 = int2d(Th)(
173 uh*vh
174 )
175 + on(1, 2, 3, 4, uh=0)
176 ;
177
178 matrix Amass = amass(Vh, Vh, solver=CG);
179 matrix Alap= alap(Vh, Vh, solver=Cholesky, factorize=1);
180
181 // Preconditionner
182 func real[int] C(real[int] & u){
183 real[int] w = u;
184 u = Alap^-1*w;
185 return u; //warning: no return of local array variable
186 }
187
188 // Solve
189 int conv=0;
190 for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++){
191 conv = NLCG(dJ, u[], nbiter=10, precon=C, veps=eps, verbosity=5);
192 if (conv) break;
193
194 alpha = df(dx(u)*dx(u) + dy(u)*dy(u));
195 Alap = alap(Vh, Vh, solver=Cholesky, factorize=1);
196 cout << "Restart with new preconditionner " << conv << ", eps =" << eps << endl;
197 }
198
199 // Plot
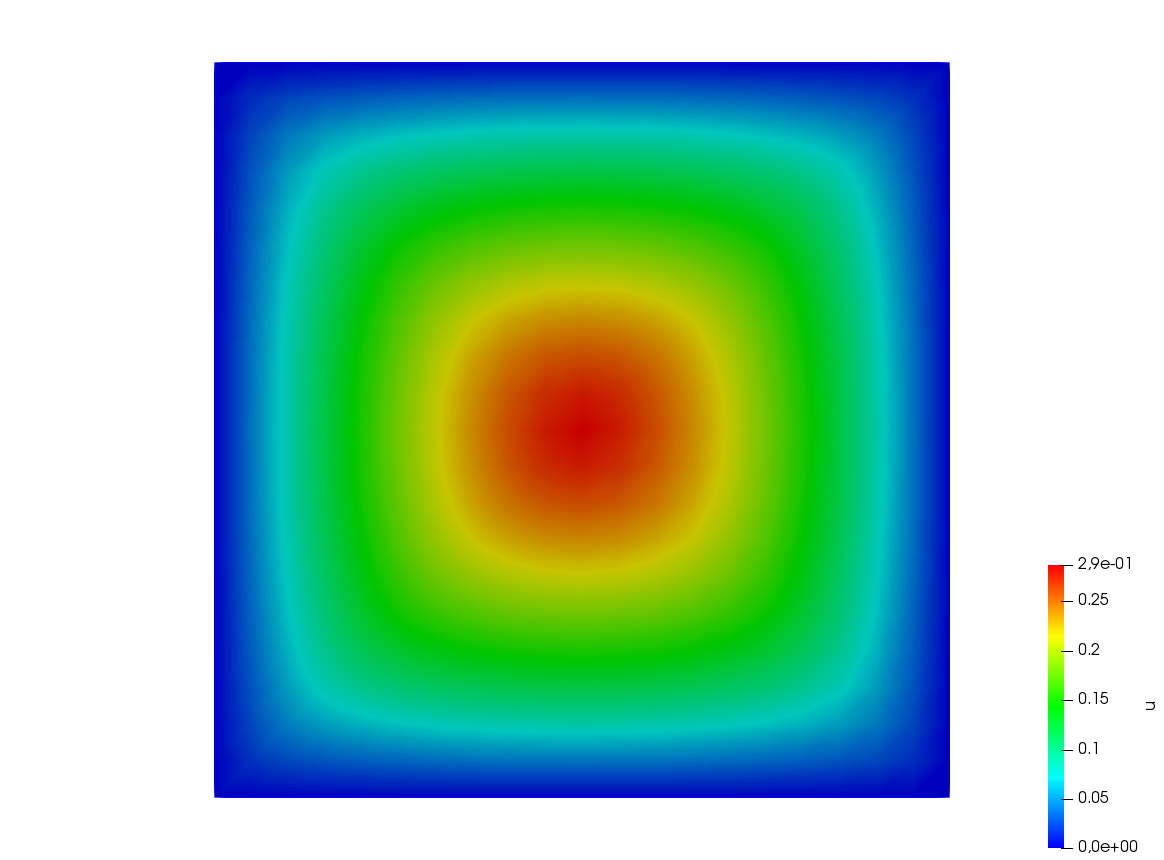
200 plot (u, wait=true, cmm="solution with NLCG");
201 umax = u[].max;
202
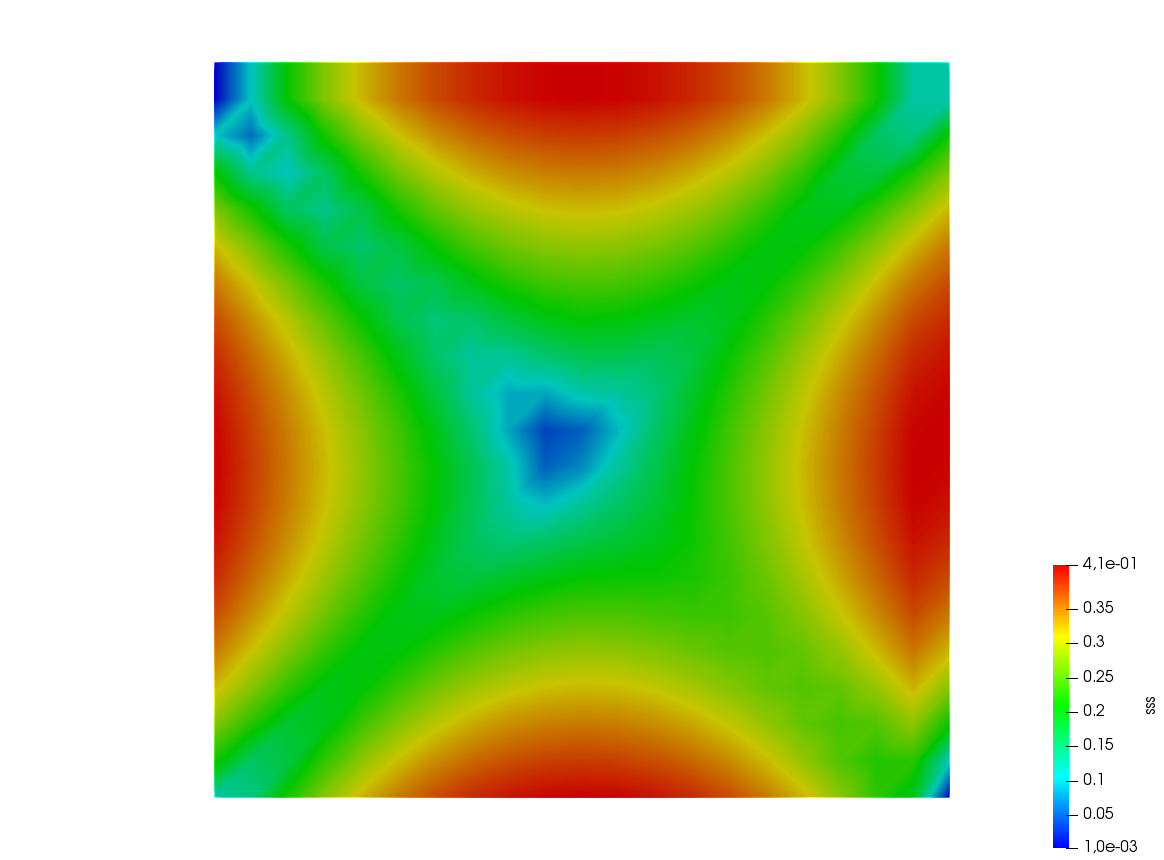
203 Vh sss= df(dx(u)*dx(u) + dy(u)*dy(u));
204 plot (sss, fill=true, value=true);
205}
206
207assert(nerr==0);
CMAES variational inequality
1load "ff-cmaes"
2
3// Parameters
4int NN = 7;
5func f1 = 1.;
6func f2 = -1.;
7func g1 = 0.;
8func g2 = 0.1;
9int iter = 0;
10int nadapt = 1;
11real starttol = 1e-10;
12real bctol = 6.e-12;
13real pena = 1000.;
14
15// Mesh
16mesh Th = square(NN, NN);
17
18// Fespace
19fespace Vh(Th, P1);
20Vh ou1, ou2;
21
22// Mesh adaptation loops
23for (int al = 0; al < nadapt; ++al){
24 // Problem
25 varf BVF (v, w)
26 = int2d(Th)(
27 0.5*dx(v)*dx(w)
28 + 0.5*dy(v)*dy(w)
29 )
30 ;
31 varf LVF1 (v, w) = int2d(Th)(f1*w);
32 varf LVF2 (v, w) = int2d(Th)(f2*w);
33
34 matrix A = BVF(Vh, Vh);
35 real[int] b1 = LVF1(0, Vh);
36 real[int] b2 = LVF2(0, Vh);
37
38 varf Vbord (v, w) = on(1, 2, 3, 4, v=1);
39
40 Vh In, Bord;
41 Bord[] = Vbord(0, Vh, tgv=1);
42 In[] = Bord[] ? 0:1;
43 Vh gh1 = Bord*g1;
44 Vh gh2 = Bord*g2;
45
46 // Function which creates a vector of the search space type from
47 // two finite element functions
48 func int FEFToSSP (real[int] &fef1, real[int] &fef2, real[int] &ssp){
49 int kX = 0;
50 for (int i = 0; i < Vh.ndof; ++i){
51 if (In[][i]){
52 ssp[kX] = fef1[i];
53 ssp[kX+In[].sum] = fef2[i];
54 ++kX;
55 }
56 }
57 return 1;
58 }
59
60 // Splits a vector from the search space and fills
61 // two finite element functions with it
62 func int SSPToFEF (real[int] &fef1, real[int] &fef2, real[int] &ssp){
63 int kX = 0;
64 for (int i = 0; i < Vh.ndof; ++i){
65 if (In[][i]){
66 fef1[i] = ssp[kX];
67 fef2[i] = ssp[kX+In[].sum];
68 ++kX;
69 }
70 else{
71 fef1[i] = gh1[][i];
72 fef2[i] = gh2[][i];
73 }
74 }
75 return 1;
76 }
77
78 func real IneqC (real[int] &X){
79 real[int] constraints(In[].sum);
80 for (int i = 0; i < In[].sum; ++i){
81 constraints[i] = X[i] - X[i+In[].sum];
82 constraints[i] = constraints[i] <= 0 ? 0. : constraints[i];
83 }
84 return constraints.l2;
85 }
86
87 func real J (real[int] &X){
88 Vh u1, u2;
89 SSPToFEF(u1[], u2[], X);
90 iter++;
91 real[int] Au1 = A*u1[], Au2 = A*u2[];
92 Au1 -= b1;
93 Au2 -= b2;
94 real val = u1[]'*Au1 + u2[]'*Au2;
95 val += pena * IneqC(X);
96 if (iter%200 == 199)
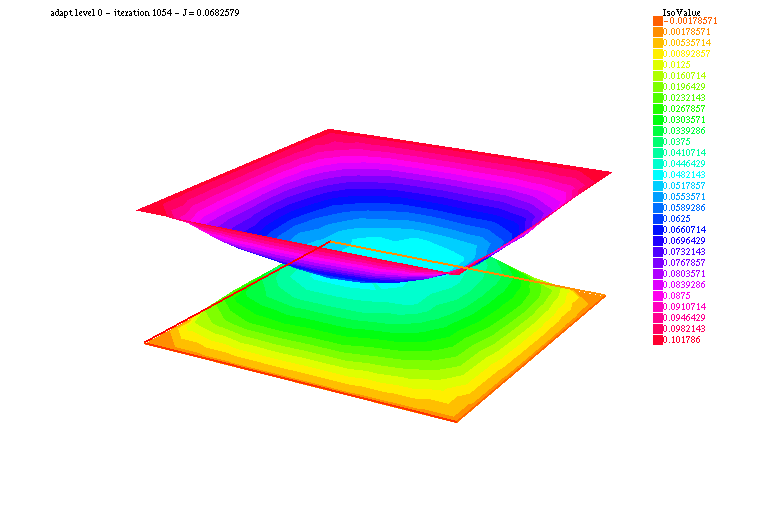
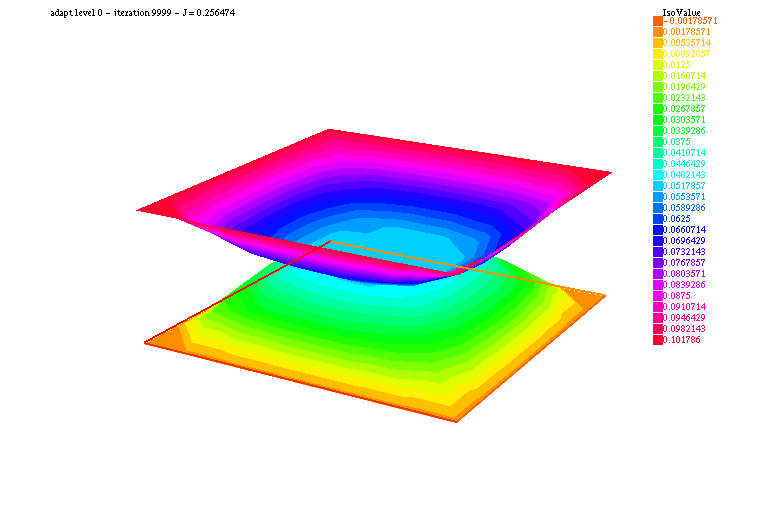
97 plot(u1, u2, nbiso=30, fill=1, dim=3, cmm="adapt level "+al+" - iteration "+iter+" - J = "+val, value=1);
98 return val ;
99 }
100
101 // Solve
102 real[int] start(2*In[].sum);
103
104 if (al == 0){
105 start(0:In[].sum-1) = 0.;
106 start(In[].sum:2*In[].sum-1) = 0.1;
107 }
108 else
109 FEFToSSP(ou1[], ou2[], start);
110
111 real mini = cmaes(J, start, stopMaxFunEval=10000*(al+1), stopTolX=1.e-3/(10*(al+1)), initialStdDev=(0.025/(pow(100.,al))));
112 Vh best1, best2;
113 SSPToFEF(best1[], best2[], start);
114
115 // Mesh adaptation
116 Th = adaptmesh(Th, best1, best2);
117 ou1 = best1;
118 ou2 = best2;
119}
IPOPT minimal surface & volume
1load "msh3";
2load "medit";
3load "ff-Ipopt";
4
5// Parameters
6int nadapt = 3;
7real alpha = 0.9;
8int np = 30;
9real regtest;
10int shapeswitch = 1;
11real sigma = 2*pi/40.;
12real treshold = 0.1;
13real e = 0.1;
14real r0 = 0.25;
15real rr = 2-r0;
16real E = 1./(e*e);
17real RR = 1./(rr*rr);
18
19// Mesh
20mesh Th = square(2*np, np, [2*pi*x, pi*y]);
21
22// Fespace
23fespace Vh(Th, P1, periodic=[[2, y], [4, y]]);
24//Initial shape definition
25//outside of the mesh adaptation loop to initialize with the previous optimial shape found on further iterations
26Vh startshape = 5;
27Vh uz = 1., lz = 1.;
28
29// Mesh adaptation loop
30real[int] lm = [1];
31for(int kkk = 0; kkk < nadapt; ++kkk){
32 int iter=0;
33 func sin2 = square(sin(y));
34
35 // A function which transform Th in 3d mesh (r=rho)
36 //a point (theta,phi) of Th becomes ( r(theta,phi)*cos(theta)*sin(phi) , r(theta,phi)*sin(theta)*sin(phi) , r(theta,phi)*cos(phi) )
37 //then displays the resulting mesh with medit
38 func int Plot3D (real[int] &rho, string cmm, bool ffplot){
39 Vh rhoo;
40 rhoo[] = rho;
41 //mesh sTh = square(np, np/2, [2*pi*x, pi*y]);
42 //fespace sVh(sTh, P1);
43 //Vh rhoplot = rhoo;
44 try{
45 mesh3 Sphere = movemesh23(Th, transfo=[rhoo(x,y)*cos(x)*sin(y), rhoo(x,y)*sin(x)*sin(y), rhoo(x,y)*cos(y)]);
46 if(ffplot)
47 plot(Sphere);
48 else
49 medit(cmm, Sphere);
50 }
51 catch(...){
52 cout << "PLOT ERROR" << endl;
53 }
54 return 1;
55 }
56
57 // Surface computation
58 //Maybe is it possible to use movemesh23 to have the surface function less complicated
59 //However, it would not simplify the gradient and the hessian
60 func real Area (real[int] &X){
61 Vh rho;
62 rho[] = X;
63 Vh rho2 = square(rho);
64 Vh rho4 = square(rho2);
65 real res = int2d(Th)(sqrt(rho4*sin2 + rho2*square(dx(rho)) + rho2*sin2*square(dy(rho))));
66 ++iter;
67 if(1)
68 plot(rho, value=true, fill=true, cmm="rho(theta,phi) on [0,2pi]x[0,pi] - S="+res, dim=3);
69 else
70 Plot3D(rho[], "shape_evolution", 1);
71 return res;
72 }
73
74 func real[int] GradArea (real[int] &X){
75 Vh rho, rho2;
76 rho[] = X;
77 rho2[] = square(X);
78 Vh sqrtPsi, alpha;
79 {
80 Vh dxrho2 = dx(rho)*dx(rho), dyrho2 = dy(rho)*dy(rho);
81 sqrtPsi = sqrt(rho2*rho2*sin2 + rho2*dxrho2 + rho2*dyrho2*sin2);
82 alpha = 2.*rho2*rho*sin2 + rho*dxrho2 + rho*dyrho2*sin2;
83 }
84 varf dArea (u, v)
85 = int2d(Th)(
86 1./sqrtPsi * (alpha*v + rho2*dx(rho)*dx(v) + rho2*dy(rho)*sin2*dy(v))
87 )
88 ;
89
90 real[int] grad = dArea(0, Vh);
91 return grad;
92 }
93
94 matrix hessianA;
95 func matrix HessianArea (real[int] &X){
96 Vh rho, rho2;
97 rho[] = X;
98 rho2 = square(rho);
99 Vh sqrtPsi, sqrtPsi3, C00, C01, C02, C11, C12, C22, A;
100 {
101 Vh C0, C1, C2;
102 Vh dxrho2 = dx(rho)*dx(rho), dyrho2 = dy(rho)*dy(rho);
103 sqrtPsi = sqrt( rho2*rho2*sin2 + rho2*dxrho2 + rho2*dyrho2*sin2);
104 sqrtPsi3 = (rho2*rho2*sin2 + rho2*dxrho2 + rho2*dyrho2*sin2)*sqrtPsi;
105 C0 = 2*rho2*rho*sin2 + rho*dxrho2 + rho*dyrho2*sin2;
106 C1 = rho2*dx(rho);
107 C2 = rho2*sin2*dy(rho);
108 C00 = square(C0);
109 C01 = C0*C1;
110 C02 = C0*C2;
111 C11 = square(C1);
112 C12 = C1*C2;
113 C22 = square(C2);
114 A = 6.*rho2*sin2 + dxrho2 + dyrho2*sin2;
115 }
116 varf d2Area (w, v)
117 =int2d(Th)(
118 1./sqrtPsi * (
119 A*w*v
120 + 2*rho*dx(rho)*dx(w)*v
121 + 2*rho*dx(rho)*w*dx(v)
122 + 2*rho*dy(rho)*sin2*dy(w)*v
123 + 2*rho*dy(rho)*sin2*w*dy(v)
124 + rho2*dx(w)*dx(v)
125 + rho2*sin2*dy(w)*dy(v)
126 )
127 + 1./sqrtPsi3 * (
128 C00*w*v
129 + C01*dx(w)*v
130 + C01*w*dx(v)
131 + C02*dy(w)*v
132 + C02*w*dy(v)
133 + C11*dx(w)*dx(v)
134 + C12*dx(w)*dy(v)
135 + C12*dy(w)*dx(v)
136 + C22*dy(w)*dy(v)
137 )
138 )
139 ;
140 hessianA = d2Area(Vh, Vh);
141 return hessianA;
142 }
143
144 // Volume computation
145 func real Volume (real[int] &X){
146 Vh rho;
147 rho[] = X;
148 Vh rho3 = rho*rho*rho;
149 real res = 1./3.*int2d(Th)(rho3*sin(y));
150 return res;
151 }
152
153 func real[int] GradVolume (real[int] &X){
154 Vh rho;
155 rho[] = X;
156 varf dVolume(u, v) = int2d(Th)(rho*rho*sin(y)*v);
157 real[int] grad = dVolume(0, Vh);
158 return grad;
159 }
160 matrix hessianV;
161 func matrix HessianVolume(real[int] &X){
162 Vh rho;
163 rho[] = X;
164 varf d2Volume(w, v) = int2d(Th)(2*rho*sin(y)*v*w);
165 hessianV = d2Volume(Vh, Vh);
166 return hessianV;
167 }
168
169 //if we want to use the volume as a constraint function
170 //we must wrap it in some freefem functions returning the appropriate type
171 //The lagrangian hessian also have to be wrapped since the Volume is not linear with
172 //respect to rho, it will constribbute to the hessian.
173 func real[int] ipVolume (real[int] &X){ real[int] vol = [Volume(X)]; return vol; }
174 matrix mdV;
175 func matrix ipGradVolume (real[int] &X) { real[int,int] dvol(1,Vh.ndof); dvol(0,:) = GradVolume(X); mdV = dvol; return mdV; }
176 matrix HLagrangian;
177 func matrix ipHessianLag (real[int] &X, real objfact, real[int] &lambda){
178 HLagrangian = objfact*HessianArea(X) + lambda[0]*HessianVolume(X);
179 return HLagrangian;
180 }
181
182 //building struct for GradVolume
183 int[int] gvi(Vh.ndof), gvj=0:Vh.ndof-1;
184 gvi = 0;
185
186 Vh rc = startshape; //the starting value
187 Vh ub = 1.e19; //bounds definition
188 Vh lb = 0;
189
190 func real Gaussian (real X, real Y, real theta, real phi){
191 real deltax2 = square((X-theta)*sin(Y)), deltay2 = square(Y-phi);
192 return exp(-0.5 * (deltax2 + deltay2) / (sigma*sigma));
193 }
194
195 func disc1 = sqrt(1./(RR+(E-RR)*cos(y)*cos(y)))*(1+0.1*cos(7*x));
196 func disc2 = sqrt(1./(RR+(E-RR)*cos(x)*cos(x)*sin2));
197
198 if(1){
199 lb = r0;
200 for (int q = 0; q < 5; ++q){
201 func f = rr*Gaussian(x, y, 2*q*pi/5., pi/3.);
202 func g = rr*Gaussian(x, y, 2*q*pi/5.+pi/5., 2.*pi/3.);
203 lb = max(max(lb, f), g);
204 }
205 lb = max(lb, rr*Gaussian(x, y, 2*pi, pi/3));
206 }
207 lb = max(lb, max(disc1, disc2));
208 real Vobj = Volume(lb[]);
209 real Vnvc = 4./3.*pi*pow(lb[].linfty,3);
210
211 if(1)
212 Plot3D(lb[], "object_inside", 1);
213 real[int] clb = 0., cub = [(1-alpha)*Vobj + alpha*Vnvc];
214
215 // Call IPOPT
216 int res = IPOPT(Area, GradArea, ipHessianLag, ipVolume, ipGradVolume,
217 rc[], ub=ub[], lb=lb[], clb=clb, cub=cub, checkindex=1, maxiter=kkk<nadapt-1 ? 40:150,
218 warmstart=kkk, lm=lm, uz=uz[], lz=lz[], tol=0.00001, structjacc=[gvi,gvj]);
219 cout << "IPOPT: res =" << res << endl ;
220
221 // Plot
222 Plot3D(rc[], "Shape_at_"+kkk, 1);
223 Plot3D(GradArea(rc[]), "ShapeGradient", 1);
224
225 // Mesh adaptation
226 if (kkk < nadapt-1){
227 Th = adaptmesh(Th, rc*cos(x)*sin(y), rc*sin(x)*sin(y), rc*cos(y),
228 nbvx=50000, periodic=[[2, y], [4, y]]);
229 plot(Th, wait=true);
230 startshape = rc;
231 uz = uz;
232 lz = lz;
233 }
234
235 regtest = rc[]'*rc[];
236}
CMAES MPI variational inequality
Command:
1ff-mpirun -np 4 CMAESMPIVariationalInequality.edp -glut ffglut
1load "mpi-cmaes"
2
3// Parameters
4int NN = 10;
5func f1 = 1.;
6func f2 = -1.;
7func g1 = 0.;
8func g2 = 0.1;
9int iter = 0;
10int nadapt = 1;
11real starttol = 1e-10;
12real bctol = 6.e-12;
13real pena = 1000;
14
15// Mesh
16mesh Th = square(NN, NN);
17
18// Fespace
19fespace Vh(Th, P1);
20Vh ou1, ou2;
21
22// Mehs adaptation loop
23for (int al = 0; al < nadapt; ++al){
24 // Problem
25 varf BVF (v, w)
26 = int2d(Th)(
27 0.5*dx(v)*dx(w)
28 + 0.5*dy(v)*dy(w)
29 )
30 ;
31 varf LVF1 (v, w) = int2d(Th)(f1*w);
32 varf LVF2 (v, w) = int2d(Th)(f2*w);
33 matrix A = BVF(Vh, Vh);
34 real[int] b1 = LVF1(0, Vh);
35 real[int] b2 = LVF2(0, Vh);
36
37 varf Vbord (v, w) = on(1, 2, 3, 4, v=1);
38
39 Vh In, Bord;
40 Bord[] = Vbord(0, Vh, tgv=1);
41 In[] = Bord[] ? 0:1;
42 Vh gh1 = Bord*g1, gh2 = Bord*g2;
43
44 //Function which create a vector of the search space type from
45 //two finite element functions
46 func int FEFToSSP (real[int] &fef1, real[int] &fef2, real[int] &ssp){
47 int kX = 0;
48 for (int i = 0; i < Vh.ndof; ++i){
49 if (In[][i]){
50 ssp[kX] = fef1[i];
51 ssp[kX+In[].sum] = fef2[i];
52 ++kX;
53 }
54 }
55 return 1;
56 }
57
58 //Function spliting a vector from the search space and fills
59 //two finite element functions with it
60 func int SSPToFEF (real[int] &fef1, real[int] &fef2, real[int] &ssp){
61 int kX = 0;
62 for (int i = 0; i < Vh.ndof; ++i){
63 if (In[][i]){
64 fef1[i] = ssp[kX];
65 fef2[i] = ssp[kX+In[].sum];
66 ++kX;
67 }
68 else{
69 fef1[i] = gh1[][i];
70 fef2[i] = gh2[][i];
71 }
72 }
73 return 1;
74 }
75
76 func real IneqC (real[int] &X){
77 real[int] constraints(In[].sum);
78 for (int i = 0; i < In[].sum; ++i){
79 constraints[i] = X[i] - X[i+In[].sum];
80 constraints[i] = constraints[i] <= 0 ? 0. : constraints[i];
81 }
82 return constraints.l2;
83 }
84
85 func real J (real[int] &X){
86 Vh u1, u2;
87 SSPToFEF(u1[], u2[], X);
88 iter++;
89 real[int] Au1 = A*u1[], Au2 = A*u2[];
90 Au1 -= b1;
91 Au2 -= b2;
92 real val = u1[]'*Au1 + u2[]'*Au2;
93 val += pena * IneqC(X);
94 plot(u1, u2, nbiso=30, fill=1, dim=3, cmm="adapt level "+al+" - iteration "+iter+" - J = "+val, value=1);
95 return val ;
96 }
97
98 // Solve
99 real[int] start(2*In[].sum);
100
101 if (al==0){
102 start(0:In[].sum-1) = 0.;
103 start(In[].sum:2*In[].sum-1) = 0.1;
104 }
105 else
106 FEFToSSP(ou1[], ou2[], start);
107
108 real mini = cmaesMPI(J, start, stopMaxFunEval=10000*(al+1), stopTolX=1.e-4/(10*(al+1)), initialStdDev=(0.025/(pow(100.,al))));
109 Vh best1, best2;
110 SSPToFEF(best1[], best2[], start);
111
112 // Mesh adaptation
113 Th = adaptmesh(Th, best1, best2);
114 ou1 = best1;
115 ou2 = best2;
116}